AWS Series: Amazon Web Services Overview
A few month ago, I have introduced with you about cloud computing. You know about three main forms of cloud computing, including IaaS, PaaS and Saas. You has been familiar with cloud provider like Amazon, Microsoft, RedHat and IBM. Today I want to give you an overview and introduction about most popular cloud provider in the world: The Amazon Web Services.
[om/content/images/2015/11/aws_overview.png)
Amazon Web Services: Overview
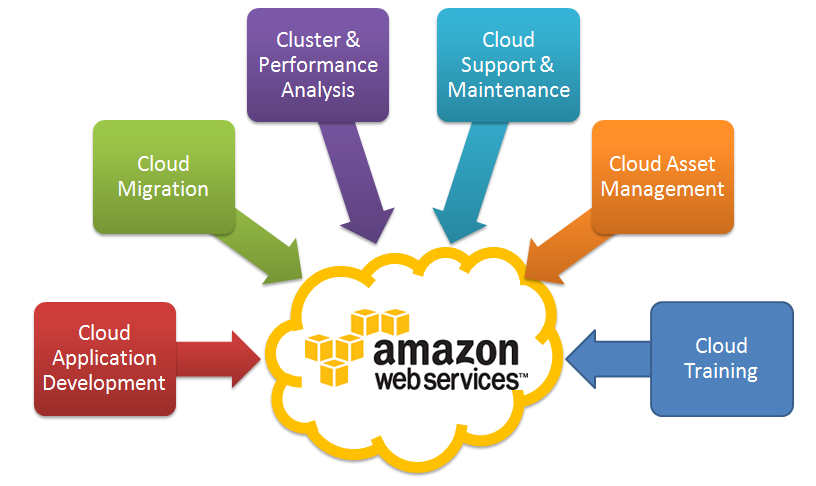
Amazon Web Services offers a broad set of global compute, storage, database, analytics, application, and deployment services that help organizations move faster, lower IT costs, and scale applications. These services are trusted by the largest enterprises and the hottest start-ups to power a wide variety of workloads including: web and mobile applications, IoT, data processing and warehousing, storage, archive, and many others. So called AWS, Amazon Web Services provides managed services and automatically maintains scaling, high availability and disaster recovery.
AWS Infrastructure
This maps gives you an overall picture about physical infrastructure of AWS:

The orange dots are AWS Regions, each Region contains one or more Availability Zones (AZs). Blue dots are Edge Location.
Amazon EC2 is hosted in multiple locations world-wide. These locations are composed of regions and Availability Zones. Each region is a separate geographic area. Each region has multiple, isolated locations known as Availability Zones. Amazon EC2 provides you the ability to place resources, such as instances, and data in multiple locations. Resources aren’t replicated across regions unless you do so specifically. Each region is completely independent. Each Availability Zone is isolated, but the Availability Zones in a region are connected through low-latency links. An edge location is where end users access services located at AWS. They are located in most of the major cities around the world and are specifically used by CloudFront (CDN) to distribute content to end user to reduce latency. It is like frontend for the service we access which are located in AWS cloud.
AWS: Services
AWS has so many services and their list is continuing expand over time. But, there are several categories which those services fall into. They are:
Core Cloud Infrastructure Services
Those services are heart of AWS as well as any cloud platform. They provides us with computing power, database management, storage services, delivery and networking. Sub-categories include:
- Compute Services: solution and services for running virtual servers on cloud. They are: AWS EC2 – Elastic Compute Cloud, ECR – EC2 Container Registry, ECS – EC2 Container Service, Elastic Beanstalk, Lambda, ELB – Elastic Load Balancing and Auto Scaling.
- Storage and Content Delivery: those services give you data storage, object replication, datawarehouse, and the highway for delivery. They are: S3 – Simple Storage Service, CloudFront for CDN, EBS, EFS and AWS Glacier.
- Database: managed service for database operation and management, including both relational database as well as NoSQL systems and even caching system. They are: RDS – Relational Database Service, DynamoDB – NoSQL Engine, RedShift and ElastiCache.
- Networking: isolation and security for IaaS. They provides network routing, policy, security and fast, reliable connection from/to AWS. They are Amazon Virtual Private Cloud – VPC, ELB and Route 53
Rich Platform Services
Based on core cloud infrastructure services, Rich Platform Services give you managed services to do analytics, build enterprise application, expand AWS to Internet-of-Things and Mobile devices.
- Analytics: AWS runs Hadoop, data pipelining, searching, streaming, machine learning and Business Intelligent services. AWS provides Elastic Map Reduce, Elasticsearch, Kinesis, Quick Sight and Amazon Machine Learning services.
- Enterprise Applications: desktop virtualization, email, calendar services and document sharing system, ready for business. They include Amazon WorkSpaces, WorkMail and WorkDocs.
- Mobility & IoT: AWS helps you with development tools, SDK, push-notification, testing, analytics, identity system. They are Mobile Hub, API Gateway, Cognito, Device Farm, SNS – Simple Notification Service and latest release with AWS IoT for connecting IoT devices to cloud.
Development and Operation Tools
They are tools and services for development, including continuous delivery and continuous integration, Git repositories; for operation, including monitoring tools, cloud automation and transformation; for security, including access management, directory service and firewall; finally, for application service, including messaging services, queueing services, workflow and email services.
Here I believe you have an overview about AWS and what they are providing. In next post in AWS series, I will give you basic idea about most popular, foundation service of AWS: Elastic Compute Cloud – EC2.